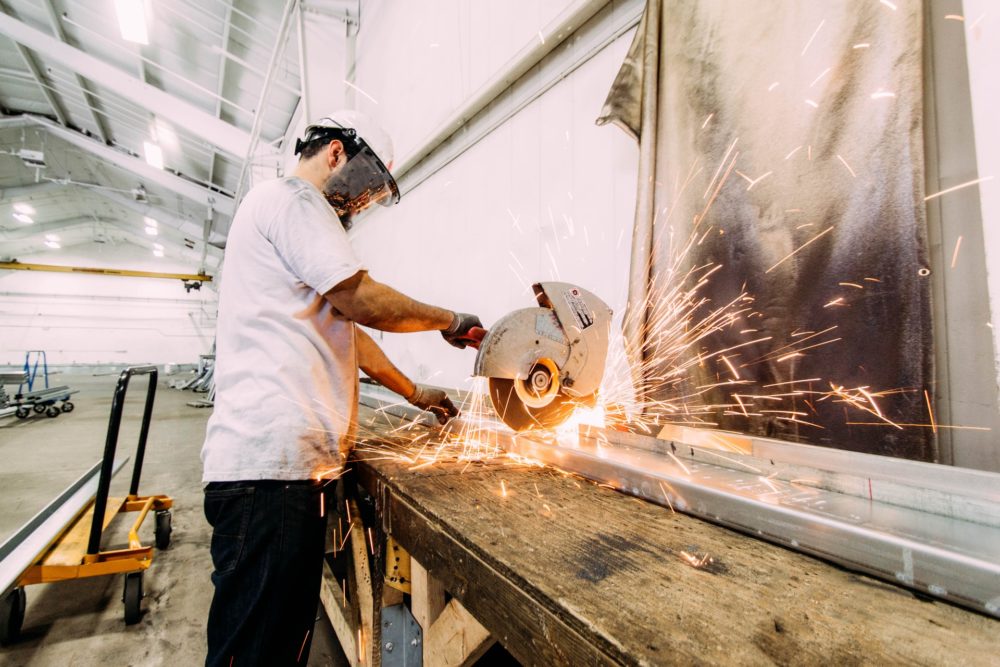
As we know, Indonesia is one of the largest countries in the world that has various important roles among countries in Southeast Asia. The country has its potential for the development of the manufacturing industry.
This sector contributes to the economic increase of 20.27% by shifting the role of Commodity-Based to Manufacture Based for the nationwide. As a result, Indonesia became the largest manufacturing base in Southeast Asia.
To complete your observation about manufacturing investment in Indonesia, we should take a look at the details below!
Introduction to Manufacturing in Indonesia
The main areas of production that most investors have been seeking out are textiles and garments, food and beverages (F&B), electronics, automotive, and chemicals. The majority of manufacturers in the sector are comprising of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises.
In the first quarter of 2020, the manufacturing industry reported a decline, with the Bank Indonesia (BI) and Prompt Manufacturing index (PMI) slipping into a contractionary phase at 45.64%. It used to be at 51.50% in the first quarter of 2019. However, all sectors nearly recorded a contraction in the first quarter of 2020, excluding F&B and Tobacco.
The most significant production volume decreased due to compressed demand and supply disruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Moreover, in the second quarter of 2020, survey respondents predicted a slight improvement in the manufacturing industry. It increased 48.79% from the first quarter of 2020 which was 45.64%. The production volume and labour utilisation were expected to improve, despite the remaining in contractionary territory.
In the last few years, most Foreign Direct Investments (FDI) have been channeled to non-manufacturing sectors. The top five destinations of FDI in Indonesia are energy, mining, chemical, real estate, and metals. Other sectors were services, such as hotels, information technology, and finance.
The average annual growth forecast from 2016-2020 is estimated at 7%, and Indonesia's proportion of GDP in the industry is higher than the rest of ASIAN, even overtaking China in 2015. Meanwhile, total manufacturing FDI from 2011-2015 is more than 76 billion dollars.
The largest manufacturing sector in Indonesia is the machinery and equipment sector. It is forecast to grow at 8% per year driven by demand from the agribusiness, energy, mining, and construction sectors.
Tin, nickel, ignite, copper, and coal, is the world’s largest production in Mining. More than half of the total demand for heavy equipment in the country comes from the mining sector. Sales of construction and mining equipment could go up to 5000 units in 2016.
Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals is the second largest manufacturing sector for FDI into Indonesia with nearly US$15 billion from 2011 to 2016, just behind the machinery and related sector.
Indonesia’s construction sector is going up 7% to 8% per year. The international tourism receipts are estimated by EIU to grow from US$9.5 billion in 2015 to US$13.7 billion in 2020. Some 50 locations in Indonesia are available for tourism development. The FDI in Indonesia’s sector from 2011 to 2015 has been over US$8 billion. As a result, it will lead to growing demand for all related machinery and equipment.
According to President Jokowi, it’s more complicated for foreign businesses to invest in Indonesia’s power sector. It is prior to a presidential directive calling for a simpler licensing process. A foreign investor would need to secure over 250 licenses, and it could take as long as 3 years to complete.
Location for Manufacturing Setup in Indonesia
Moreover, infrastructure is one of the salient variables for investments, with significant profit implications. Indonesia has underinvested in public infrastructure, and it’s leading to a growing infrastructure deficit.
The Government of Indonesia (GoI) recognized that the infrastructure deficit as a national priority with the National Medium Term Development Plan (RPJMN) estimates IDR 5.4 trillion (USD 415 billion) is an additional investment in infrastructure from 2015 to 2019.
Despite the infrastructure deficit, Indonesia currently has 11 Special Economic Zone (SEZ) across the country with investment opportunities available in agriculture, manufacturing, tourism, and natural resources.
In 2019, three SEZs were created, while in 2020 another seven in the development phase. These newly launched SEZ aim to bring at least US$50 billion over the next 10 years. Until October 2019, the total investments SEZ of Indonesia have achieved over US$6 billion.
Most SEZs are planned as industrial zones to promote manufacturing activities and attract foreign investment. 8 of SEZs have been established by the government regulation, and they are eligible for special economic incentives.
6 of the locations including, Sei Mangkei, Tanjung Api-api, Maloy, Palu, Bitung, and Morotai, focus on a mix of natural resource processing industries, mining and agricultural industries. Meanwhile, the 2 others, Tanjung Lesung and Mandalika, focus on tourism and ecotourism activities.
To support more of the manufacturing activities, the government plans to provide the tax holidays rules on facilities constructions on SEZs, as well as to offer more tax incentives.
After knowing the location of manufacturing setups in Indonesia, you might be curious how to establish a company in the country. Let’s follow the details below!
Corporate Establishment in Indonesia
There are two investment options for foreigners to establish a corporation in Indonesia.
- The first one is Limited Liability Company (PMA).
PMAs can operate as a limited liability company, and the most well-known form of foreign investment. PMA licenses acquired through the Indonesian Investment Coordinating Board (BKPM), yet require a huge capital investment and take more time to process. PMA also gives investors full authority over the course of the organization and decreases the dangers of finding an appropriate partner.
- The second one is Representative Office.
A representative office has no capital requirements and sets aside less effort to set up as it cannot take part in business exercises. The role of the representative office is limited to liaison and representative of the interest of the parent company.
After knowing the investment options, then you need to know the steps to establish the corporation.
Steps To Manufacturing The Corporate Establishment
Step 1: Deed of Establishment
The initial step is to decide the level of the permitted remote responsibility for arranged business exercises. Then, you need to pick a name for your PT PMA, the name needs to include at least 3 words and cannot be misleading or similar to some other existing organization or government establishment’s name.
The corporate’s activities and purpose must be determined in its Articles of Association within the Deed of Establishment, which must be made before a notary. The Deed of Establishment should be approved by the Ministry of Law and Human Rights. This also implies your organization is legitimately set up under Indonesian Law.
Step 2: Domicile and Tax Registration
After the Ministry of Law and Human Rights has approved your Deed of Establishment, the next stage is to get a Domicile Letter (Surat Keterangan Domisili) from the regional government and acquire a Tax Identification Number (NPWP - Nomor Pokok Wajib Pajak) from the local tax office.
Step 3: Identification Number to Operate (NIB-Nomor Induk Berusaha) and Operational License/Commercial License
A unique identification number, NIB, will identify your company profile in Indonesia and it will also serve as your import license (previously API-U), customs identification number (previously NIK), and business registry (previously TDP).
Registration of your legal entity to OSS also automatically registers your PT PMA under the Indonesian Health and Social Security System (BPJS Kesehatan, BPJS Ketenagakerjaan).
Step 4: Operational License/Commercial License
The business’s operational license/commercial license is usually issued on the same day as NIB. In cases like this, it can take months before the government grants your business a license.
Step 5: Application For Permanent Business License
Once you are issued the above principal license, you are expected to start constructing the factory. Once at least 80% of the machinery is installed, the company is required to apply for a permanent business license. But, it shouldn’t be more than 3 years after the principal license is issued.
Step 6: Open a Bank Account
The process of opening a corporate bank account in Indonesia varies slightly from bank to bank. You need to present the documents after your PT PMA registration is complete in order to set up an account. The documents are:
- Copy of PT Tax card (NPWP)
- Copy of PT Domicile letter
- Copy of BKPM Investment registration Letter (SIUP)
- Copy of Deed of Establishment (AKTA)
- Copy of ID card of all board of directors, shareholders, and authorized signers
- Copy of Company registration letter (TDP)
- Copy of PT deed of establishment’s approval from the Ministry of Law and Human Rights (Pengesahan KEMENKUMHAM)
Step 7: Register to the Ministry of Manpower
Hiring team for factory installation, including foreign workers who can be granted working visas. Remember that the working visa can only be issued to foreign workers whose competence is needed to assist the installation of the factory. Only specific job titles are allowed by the Ministry of Manpower.
Step 8: Application for API-P (import identification number)
As a manufacturing company, you get a special import license API-P which allows you to import any products that are required to set up your factory. This makes API-P different from API-U which would only allow you to import products from one category.
You are not allowed to import products for selling them in Indonesia with this license. API-P will be accompanied by NIK (custom identification number).
Step 9: Masterlist Application
As a manufacturing company, you are entitled to apply for an exemption of import tax for the machinery you need for production. Such exemptions are given based on the presentation in front of BKPM by the Board of Directors of the company.
These are all the details about guides to manufacturing investment in Indonesia. Hopefully, with this article, you will be attracted to establish foreign companies in the country. However, if you need more information about this, you can contact us. Remember, Viettonkin will always be ready to assist you!
Nowadays, Indonesia becomes more popular with foreign direct investment players who want to enter the Asia market, as the country marks the 16th largest economy in the world in 2019. It causes many foreign investors to set their eyes to expand their businesses to Indonesia. Entering Indonesia’s market somehow will offer significant results for foreign direct investment players.
Before getting into deep about how and why foreigners should expand their businesses to Indonesia. It’s better to take a look at Indonesia’s economy first.
Overview of Indonesia’s Economy in General
As stated by the World Bank and projections from Trading Economics, Indonesia’s GDP was US$1126 billion back in 2019. Indonesia’s GDP accounts for 0.93% of the world economy. In fact, Indonesia’s GDP has continuously grown since 2015.
Furthermore, according to the new Asian Development Bank (ADB) report, Indonesia’s economy is expected to grow by only 2.5% this year, and it’s a four-year low of 5.02% in 2019. The COVID 19 outbreak situation gave an impact to this country’s economy. However, it is expected to gradually improve in 2021.
The ADB report also says the domestic demand is expected to weaken, as business and consumer sentiment decreases. As the global economy will recover next year, Indonesia’s growth also hopes to gain momentum, with recently introduced investment reforms providing an additional stimulus.
The report says, the inflation which averaged 2.8% last year, is forecast to increase to 3% in 2020, before it might be declining to 2.8% in 2021. The inflationary pressure from tight food supplies and currency devaluation is expected to be partially counterbalanced by lower prices for non-subsidized fuel, as well as subsidies for electricity and food.
According to the World Economic Forum’s Global Competitive Index in 2019, Indonesia is in the 4th place within ASEAN region, behind Singapore, Malaysia, and Thailand. The Indonesian economy has been climbing steadily higher in the ranks of the moderately free, and it makes Indonesia a promising country for the foreigner entrepreneurs to expand their businesses here.
Indonesia’s government is expected to continue efforts to encourage more private investment in infrastructure and manufacturing. The government can achieve that goal by modernizing and simplifying investment regulations, and they also need to ensure the labor market controls, such as minimum wages, which will give an effect to employment growth.
The World Bank report says, Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) net inflows in Indonesia in 2019 was US$24.4 billion. It increased by 29% compared to the previous year. However, the FDI net outflows in 2019 was US$4.392 billion.
In the March quarter of 2020, due to ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, FDI to Indonesia slumped 9.2% year-on-year to US$6.4 billion (IDR 98 trillion), it is the lowest amount in 6 months to 1 year, if it compared with a 6.4% growth in the previous period. It all happened as the investors delayed business decisions due to the outbreak.
The leading sectors for FDI projects in Indonesia are trade and reparation, such as hotel and restaurant, chemical and pharmaceutical, Hosing, Industrial Estate, and office building. Meanwhile, the leading locations are Special Territory of Jakarta, West Java, and East Java.
There is a lot of potentials to grow the business and join the market here before the competitors enter. You might ask yourself why you should expand, or what are the opportunities for growing the business. Moreover, let’s check the details for the foreign direct investment in Indonesia below.
The Opportunities For Foreign Direct Investment in Indonesia
Indonesia renewed its Investment One-Stop Service (OSS) Centre on 26 January 2015, in which investors can now process their investment licenses and other related licenses in one office.
The centre is integrated with 22 ministries and agencies, and it covers the licensing processes for most of the business fields. Investors can also monitor the progress of their business license application online, and ensure that the deadline complies with Standard Operating Procedures (SOP).
By looking at how Indonesia has a lot of potential for more FDI projects, President Joko Widodo is expected to continue driving forward with large-scale developments, while the country is also attracting financial support from China for major infrastructure works under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
The government plans to spend US$40 billion (IDR571 trillion) on the development of transport infrastructure in Jakarta by 2029. Announced in March 2019, the government aims to build a 120km light transit railway corridor in the capital city. In addition, in May 2019, the government announced plans to invest US$412 billion (IDR6 quadrillion) to develop Indonesia’s overall infrastructure during the period of 2020-2024. It includes the construction of 25 new airports, highways, affordable houses and power plants.
A study by Polling Indonesia had cooperated with the Indonesian Internet Providers Association (APJII) reported that, there are 171 million people, or 64.8% of the total population of 264 million Indonesians, were already connected to the internet in 2018. It represents an increase from 54.86% in 2017. It makes Indonesia become one of the top ten most improved countries in the Mobile Connectivity Index. This improvement has been broad and driven by better performance across all four enablers: infrastructure, affordability, consumer readiness, content and services.
With all of these opportunities, it can attract more FDI projects to Indonesia. But, in fact, there are some challenges that foreigners need to know as well.
The Challenges For Foreign Direct Investment in Indonesia
According to Transparency International’s Corruption Perception Index 2019, Indonesia ranks 85th out of 183 countries. However, that would mean foreign investors might have a few obstacles in building an investment climate in Indonesia, such as conflicting regulations, rigid labor laws, legal unpredictability, the rising cost of credit, and contract issues.
The World Bank reports and findings of Transparency International suggest corruption and inflexible domestic regulations have significantly affected both domestic and foreign investment in Indonesia.
Despite the challenges, Indonesia still has more opportunities and potential for foreigners to take and build a business here. As the country's infrastructure is growing, it will continue attracting more FDI projects to bring in Indonesia.
Additionally, you might be curious if it’s easy or complicated to expand the business here, but you should not be worried about that. As long as you meet the requirements, you will be fine.
The Requirements To Expand Businesses in Indonesia
Indonesia has several types of companies, which sometimes confuse foreign investors when choosing the most suitable for their business activities. See the details where we describe the differences in the type of company setup options in Indonesia!
1. The Indonesian Limited Liability Company (PT)
- Minimum Capital: it depends on Business License (SIUP) Categories.
- 100% local share
- The company is eligible to conduct business up to 3 different business lines.
- Minimum paid-up capital for Small SIUP is IDR 50.000.000 - IDR 600.000.000
- Minimum paid-up capital for Medium SIUP is IDR 600.000.000 - IDR 10.000.000.000
- Minimum paid-up capital for Large SIUP is above IDR 10.000.000.000
- Can be sponsor company of KITAS
- Minimum 2 shareholders, 1 Director, and 1 Commissioner
2. PT PMA (Penanaman Modal Asing) or Foreign Investment Company
- The minimum investment plan US$1 million
- The minimum paid-in capital US$250.000
- Shareholder: based on the negative investment list
- In the form of a limited liability company, which can perform complete business activities in Indonesia, includes generating revenue
- Has the same rights and responsibilities as a local company
- Only allowed to operate in 1 specific business area
- Minimum 2 shareholders, it can be individuals or legal entities
- Minimum organizational structure, 1 Director, and 1 Commissioner
- Minimum investment plan is over US$1 million
- Minimum paid-up capital is US$250,000
- The company can sponsor many foreign employees
3. Representative Office (KPPA)
- No Minimum Paid Capital Required
- Shareholder: Based on the negative investment list
- In the form of a branch office from the parent company overseas
- Activities are limited to marketing, research and promotion. It means that the representative office is not allowed to generate revenue or to conduct direct transactions in Indonesia. The transaction goes directly to company headquarters.
- There is no shareholder requirement
- There is no Director and Commissioner requirement
- There is no capital requirement
- Limited sponsorship of foreign employees, at least Chief of Representative Office and Assistant of Chief of Representative Office
These are all information about entering the market in Indonesia. You should pay attention to details, and complete all the requirements once you choose the legal entities for your business activities. If you are unsure about all these things, you can contact us anytime. Viettonkin will always be ready to assist you!
The Coronavirus pandemic is like a hurdle that prevents the development of the majority of industries. Although the insurance industry is not affected immediately like the tourism or F&B sector, the industry, to some extent, suffers from the chain effect due to the shift in consumer behaviour. The article will provide you information about the insurance industry in Vietnam before and during the Coronavirus pandemic and illustrate how it responds to the situation.
The insurance industry in Vietnam before the Coronavirus pandemic
So how’s about the actual situation of the Insurance industry in Vietnam before the Coronavirus pandemic? This section provides you with statistics and information about market share and customers’ trend in the Vietnamese insurance industry in general.
In terms of the market share, according to the Department of Insurance Supervisory Authority, the revenue of insurance payment reached more than 133 billion VND in 2018, more than 24% in 2017. The lifetime insurance gained 87.960 billion VND. In five consecutive years, the insurance market in Vietnam had gained revenue of over 20%. In addition, the share in the revenue of insurance payment belongs to five biggest insurance companies in Vietnam including Bao Viet Life Corporation, Dai-ichi, Manulife, Prudential and AIA with 2541%, 15.89%, 12.8%, 12.7%, and 10.63% respectively.

It was predicted that the growth rate of lifetime would remain from 11% to 12% and the combined rate will be kept at a high level of around 98%. Another factor that will influence the insurance businesses is the tendency of interest decline for banks, from 0.25% to 0.3 %. As a result, the insurance company of BIDV (BSC) decided to lower the investment score of non-life insurance from “Positive” in 2019 to “Neutral” in 2020.
Regarding to Vietnamese customers, based on the registered forms, the portion of Vietnamese people buying life insurance is 8.5%, but in fact, the actual number may be lower because an individual can have a lot of life insurance contracts. Moreover, 53% of surveyed participants said that they were considering whether they bought insurance or not. The reason for a half of participants considering refers to the price of life insurance. To participants, the price is too high for them to pay.
Besides the market share, the Vietnamese insurance industry also gains advantages and disadvantages when the CPTPP agreements have become effective. These agreements bring opportunities such as extending the market into foreign countries, diversifying insurance products, improving the quality of human resources, and boosting the reputation of insurance corporations. On the other hand, potential challenges can be high competitiveness among companies in Vietnam and in foreign countries, the unstable development of this industry as well as the gap in risk management between Vietnamese and foreign companies.
These are general information relating to the Vietnamese insurance industry before the Coronavirus pandemic. What’s about the shift in this industry during the pandemic? Let’s follow the next part.
The insurance industry during the Coronavirus pandemic
Coronavirus pandemic impacts
If the pandemic lasts for several months and breaks out in many places across Vietnam, insurance enterprises have to pay more compensation for insurance, which may affect negatively the business. According to the Ministry of Finance, insurance companies are affected but do not suffer from a huge loss like other sectors such as F&B and tourism. Regarding to non-life insurance, the revenue of insurance payment does not fluctuate because these contracts are reinsured in the previous year namely property insurance, responsibility insurance, health insurance and so forth. In the short-term, payment of tourism insurance and compensation for business disruption are not too high and health insurance has not raised for patients infected with COVID-19. These payments is under social insurance.
Actions of insurance companies
What do insurance companies do during the Coronavirus pandemic? Vietnamese insurance enterprises offer supporting policies for customers. For instance, Buu Dien Insurance Company offers a compensation package up to 15 million VND in case he or she is infected with Coronavirus, Bao Minh Insurance company extends regulations for tourism insurance for those who are unfortunately infected with COVID-19 while traveling, Bao Viet Life Corporation launches a campaign supporting 20 million for each case being positive with Coronavirus and the campaign is available for the first 1 million registers. Besides, some other companies introduce new products to assist people amid the peak of Coronavirus. The majority of these products aim to help the community rather than gaining profits.
Furthermore, insurance products relating to the Coronavirus are sold well. PVI insurance company reported that one business has bought the Coronavirus insurance for more than 1,000 employees. Plus, VietinBank insurance has sold more than 3,000 insurance contracts related to the Coronavirus, in which businesses account for 15%.
Government policy
However, the Vietnamese government (the Ministry of Finance) requested insurance companies not to introduce or implement Coronavirus insurance since March 31. If these products are being sold, it is likely to have risks for insurance enterprises in case the pandemic has no positive signals.
Case study: Manulife Vietnam responds during the Coronavirus
Manulife Vietnam is a foreign-invested company in Vietnam since 1999 and also one of the biggest enterprises in the Vietnamese insurance industry.
Similar to many other businesses, Manulife Vietnam is affected by the Coronavirus pandemic. What are they doing to respond to the pandemic? This part will discuss Manulife Vietnam’s marketing campaign on social media.
Since the Coronavirus outbreak, Manulife Vietnam usually published content posts related to healthcare tips and health insurance products for users. On 18 February - when the cases infected with COVID-19 under 20 cases, Manulife Vietnam educated users how to exercise at home or how to improve the immune system.


At this time, the insurance company boosted products named “Sống khỏe mỗi ngày” (Be healthy every day) with great features and considerable discounts such as healthcare support for those receiving treatments at patient’s department, outpatient’s department and odontology, reimbursement up to 15% if users register family healthcare insurance and professional healthcare consultancy service 24/7.
Besides, Manulife Vietnam also shared information about how to wash hands and how to protect your health when you are in public places. These pieces of information were extracted from the official guideline of the Ministry of Health, hence assist users in exposing to the trustworthy information amid fake news floating on social media.
On March 9 (after the first case infected with COVID 19 in Hanoi), Manulife Vietnam introduced e-pay with insurance registers in three simple steps. The insurance company encouraged customers to use cashless payment and request the compensation via online payment method. This action, can be said that, is an effective measure to ensure the safety for both customers and employees during the Coronavirus pandemic.

Three steps to access the online payment method on Manulife’s website.
Furthermore, like many other brands, Manulife Vietnam also sent sincere thanks to doctors, nurses and police who were trying their best to control and fight against the pandemic at the frontline. They are heroes wearing blouses, their weapons are not guns, but their willingness and determination.

Thanks doctors, nurses and polices for assisting Vietnam in fighting the invisible enemy.
Additionally, the business joins hands with the authorities by sponsoring 3.2 billion VND for medical equipment including face masks, medical protective clothing, hand sanitizers and fans. These types of equipment are transported to quarantine areas to support residents and doctors.

When the policy of social distancing becomes effective, Manulife Vietnam shares interesting tips to work from home or exercises at home.
How’s about other industries during the pandemic? You can read here.
In conclusion, the Coronavirus pandemic has influenced a lot of businesses negatively and somehow positively. During this situation, it is required that enterprises have quick responses to deal with challenges. The insurance sector, in general, has offered new products for those who are unfortunately infected with the COVID-19 or updated online payment method to avoid crowds. Manulife Vietnam is a typical example of how the company reacts with the situation. Hope that you have got certain ideas about the Vietnamese insurance industry.

Thanks to the diverse culture, splendid landscape, up-and-coming cities, and lovely beaches, Vietnam becomes an attractive tourist destination in Southeast Asia. Tourism and hospitality develop parallelly, hence when tourism thrives, hospitality grows, especially accommodation. This article will provide you a brief outlook about Vietnamese high-end hotels and reasons why you should invest in hotel real estate.
Vietnam hotel industry outlook for 2020
The hotel sector has boomed for the last three years. Vietnam has been an affordable tourism destination in foreign visitors’ eyes, hence the number of travelers coming to our country reached 8.5 million in the first six months of 2019. Thanks to a large number of domestic and foreign visitors, the hotel market in Vietnam is also extending. Hotel performance is much more diversified within Vietnam from Ho Chi Minh City to Cam Ranh in the South to Da Nang and up to Hanoi in the North.
By the end of the third quarter of 2019, it is estimated that more than 442 four-star and five-star hotels were opened in Vietnam, increasing 21% annually each year since 2015 (called a compound annual growth rate - CAGR). Da Nang and Khanh Hoa - the two most favourite destinations - led the supply of upscale hotels with a growth rate of 19% in each city, followed by Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi.
In addition, revenues for high-end hotels rise dramatically in 2019. According to the newly-released Hotel Survey 2019 by Grant Thornton, the revenue per room grew by 5.4% from 2017 to $83.4 in 2019. Kenneth Atkinson, the senior board adviser of Grant Thornton Vietnam, confirmed that the average occupancy rate at 5-star hotels remained at a high proportion of 75.6%.

The chart shows the average occupancy room rates at 4-star and 5-star hotels in Vietnam.
The revenues from luxurious hotels increase gradually year by year, which may indicate the higher number of tourists staying at high-end hotels then there is a potential for opulent accommodation.
It is predicted that the earnings from the hotel sector in 2022 can be double the revenues in 2017, to more than US 890 million.
Reasons why you should invest in the hotel sector
Impressive demand growth for hotel
Obviously, the higher number of tourists will boost the higher demand for accommodation, especially luxurious hotels and resorts.
International tourists arriving in Vietnam has accelerated considerably, reached a remarkable growth of 21% within 11 months of 2018. In addition, the growth rate of foreign visitors arrivals also increases in the decades, which is two times higher than the Asia Pacific annual growth rate.
Furthermore, outbound travelers come to Vietnam from a variety of countries. Visitors from Asia accounted for the large proportion of foreign tourists in 2019 with over 81%, of which Chinese visitors reached more than 5.2 million and Korean tourists reached more than 3.2 million. Tourists from Europe, America, Oceania, and Africa also increased by 13.4%, 10.2%, 0.4%, and 19.8%%, respectively, annually.
Vietnam is a good place for MICE and event organization

Sofitel Metropole Hanoi - a place holding Trump-Kim meeting.
Vietnam has been chosen as a host for a lot of business conferences, meetings, and summits. When important events are organized in Vietnam, it definitely motivates entrepreneurs, visitors, and delegates to come to the destination. For example, the Trump-Kim summit in Vietnam in February 2019 had positive impacts on Vietnamese tourism. At that time, five-star hotels in Hanoi run out of rooms to rent. Just a week before the summit took place, a lot of high-end hotels such as Grand Plaza, Hilton, Intercontinental, Sofitel Metropole, Sheraton, and JW Marriott announced that no more rooms were available from Feb 25 to the end of the month. In the near future, Vietnam will be the host of SEA games 31 in 2021. This event will attract many news reporters, Asian people to come here to encourage sports teams and it is forecasted that hotel owners will earn huge revenues and gain more profits.
Favourable geography and low-cost air ticket
Vietnam’s rich geographic, topographic diversity and local climate are advantages that Mother Nature endows us. Favourable climate conditions support a variety of tourism appeals. Where tourism develops, there are a lot of hotels and resorts. Popular tourism destinations in Vietnam are Da Nang, Hoi An, Nha Trang, Phu Quoc, Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh, Ha Long and so on. Coastal cities like Da Nang, Nha Trang, and Phu Quoc island impress foreign visitors with crystal-clear water, stunning beaches, beautiful landscapes, and friendly people. In these cities, a lot of luxurious hotels and resorts of prestigious brands namely Silk Path, InterCon, JW Mariott, FLC group… are built and invested to provide spaces for entertainment such as golf courses. It is predicted that real estate for hospitality at these places continues to attract many foreign investors.
Government support
The Vietnamese government has provided infrastructure improvements with new international routes to encourage tourism as well as enable Vietnam to transform from Experience Destination to Holiday Destination with repeated guests. Besides, the government also approves gambling in the casino under certain conditions. This new regulation supports hospitality growth and widens the regional competition.
Technology application boosts Vietnam hotel tourism and hospitality
The Vietnamese government plans to target USD 45 billion in tourism revenue in 2025. In order to achieve the target, technology application is one of the priorities.
Industry 4.0 with its advanced information technology has paved the way for Vietnam tourism and hospitality. Traditional tourism will transfer to smart tourism. Technology allows travelers to book flight tickets, accommodation online while searching for places to enjoy the local cuisine without depending on travel agents.
Technology application is being indeed developed but it is now available in major cities. The application in hotels in remote areas is still somehow limited, therefore the investment required to develop smart applications can be huge.
Moreover, artificial intelligence in hospitality can be a fertile ground to improve the competitiveness among luxurious hotels within Vietnam as well as in the region. The wow factor of AI application in hospitality is obvious. AI, in particular Face ID, allows visitors to check out in 3 seconds or paying supplement services quickly and high personal information security. In Vietnam, Vinpearl is the first hospitality company to apply facial recognition technology.
In addition, you can look FDI guide in Vietnam at Viettonkin's blog.
To sum up, hospitality in Vietnam has a huge potential for foreign investors. Vietnam tourism and hospitality are on the way of fast-speed development with a lot of advantageous factors regarding demand growth, endowed geographic, an ideal place for big event organization and government support. Thanks to the technological application, hospitality in Vietnam is predicted to develop further in the near future.
(more…)

Due to the spending power of the Indonesian middle class, Indonesia is a good place to establish or expand a franchise. It is a safer alternative option to start your business.
Although the demand for a franchise business is high, the franchising regulatory is still complex. Investors need to go through bureaucratic procedures. There are some points you need to know before starting this business!
Best Possible Franchise businesses:
- Food
- Entertainment
- Coffee joints
- Beauty & Fitness
- Retail
- Digital Agencies
- Education
- Language centers!
Conditions to start the franchising business
| Franchise |
Franchisor |
| Have specific business characteristics |
5 years experience in the business |
| Has been proven to generate profits |
Does not necessarily need a legal entity |
| Have easy to learn & applied SOP on quality and service |
Must have SOP |
| Must have registered Intellectual Property Rights |
Capable to provide continuous support to the franchises |
| Needs to apply for licenses according to the activities |
|
| Can sell supporting service or products, under 10% from the actual given license |
|
Settle franchise agreement
- Provide prospect of an offer to franchisee 2 weeks before signing
- The prospect offer and agreement have to be in Bahasa Indonesia
- Based on Indonesian Law
Obtain a Franchise Registration Certificate (Surat Tanda Pendaftaran Waralaba/STPW)
If you want to know clearly the procedure to set up your company in Indonesia, feel free to contact us!

Batam is Indonesia’s first Special Economic Zone (SEZ). It locates on Straits of Melaka, the second busiest sea traffic in the world after the Strait of Hormuz in the Persian Gulf. Here are key benefits of doing business in Batam:
- Physical infrastructure in Batam is better than in the rest of Indonesia. It is easy to move materials, equipment and finished product into or from Batam’s port and airport compared to other parts of Indonesia.
- Basic infrastructure like electric power and water is the same as what is available in Jakarta.
- Batam is very close to Singapore, only 20 km away. Investors can go to Singapore if the facilities are lacking in Batam only by ferry.
- Batam is bordered by Malaysia and Singapore.
- Batam has a one-stop policy for investment procedures. Investors can do all its business transactions through a single office. The process will not take longer than 20 working days.
- Tax incentives offered in Batam. Most of the transaction to goods and services are free from VAT and LST but investors need to follow several administrative requirements, such as Business License from BPK, Goods need to relate to business activities and approve by the BPK, etc.
- Batam has been a promising place for the electronics manufacturing industry. Batam has attracted many electronic industry giants, namely Sanyo, Panasonic, Siemens, Sony, and Phillips.
Interested in doing business in Batam? Contact us!
 English
English























